What are the main components of an electric vehicle drivetrain?
The drivetrain of an electric vehicle (EV) comprises several main components that work together to convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy that propels the vehicle. Here are the key components of an electric vehicle drivetrain:
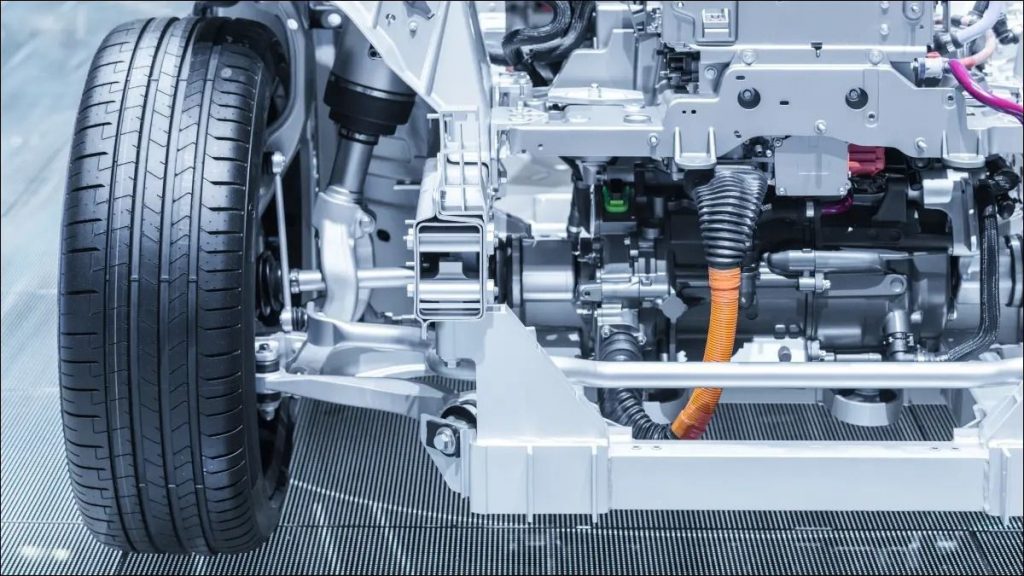
- Battery pack: The battery pack is the primary energy storage system in an EV. It consists of multiple individual battery cells, typically lithium-ion, assembled into modules. The battery pack stores electrical energy and supplies it to the electric motor when needed.
- Electric motor: The electric motor is the primary source of propulsion in an EV. It converts electrical energy from the battery pack into mechanical energy, which drives the wheels. There are different types of electric motors used in EVs, such as permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSMs), induction motors, and switched reluctance motors (SRMs).
- Motor controller: The motor controller acts as the “brain” of the drivetrain, managing the flow of electrical energy from the battery pack to the electric motor. It regulates the motor’s speed and torque by adjusting the voltage and current supplied to the motor based on the driver’s inputs (such as the accelerator pedal) and the vehicle’s operating conditions.
- Transmission: The transmission in an EV is typically much simpler than that found in an internal combustion engine vehicle. Many EVs use a single-speed reduction gearbox, which transfers the torque generated by the electric motor to the wheels. This is because electric motors have a wide range of operating speeds and can deliver maximum torque from a standstill, eliminating the need for a complex multi-speed transmission.
- Power electronics: The power electronics in an EV include components such as the inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) from the battery pack into alternating current (AC) to power the electric motor. It also includes the onboard charger, which converts AC from the charging station into DC to charge the battery, and the DC-DC converter, which steps down the high-voltage DC from the battery pack to a lower voltage to power the vehicle’s auxiliary systems, such as lighting and infotainment.
- Regenerative braking system: As previously mentioned, the regenerative braking system recovers kinetic energy during deceleration or braking and converts it into electrical energy to recharge the battery. This process enhances the overall efficiency and driving range of the EV.
These components work together to provide a smooth, efficient, and responsive driving experience in electric vehicles, while reducing emissions and operating costs compared to internal combustion engine vehicles.


